From thick hair to strong bones: 10 benefits of eating eggs daily
Eggs are nutritional powerhouses, packed with vitamins, protein, and healthy fats, offering numerous health benefits. Regular consumption supports heart health by boosting good cholesterol, enhances brain function with choline, and promotes eye health with antioxidants. Furthermore, eggs contribute to stronger bones, healthier hair and skin, weight management, muscle strength, a robust immune system, and increased levels of good cholesterol.

Eat your eggs, especially if you enjoy them. Unless you are a vegan or vegetarian, eggs are among the most nutrient-rich foods you can include in your diet. They provide a good source of protein and are packed with vitamins and healthy fats. Enjoy them boiled, scrambled, or sunny-side up. Here are several advantages of incorporating eggs into your regular diet.
Eggs: A Nutritional Goldmine
Consider eggs as superfoods. They are a powerhouse of vitamins. One egg contains 78 calories, 6 grams of protein, and 5 grams of fat.
A single large boiled egg provides:
- Vitamin A: 8% of the Daily Value (DV)
- Folate: 6% of the DV
- Pantothenic acid (vitamin B5): 14% of the DV
- Vitamin B12: 23% of the DV
- Riboflavin (vitamin B2): 20% of the DV
- Phosphorus: 7% of the DV
- Selenium: 28% of the DV
- Eggs also contain notable amounts of vitamin D, vitamin E, vitamin B6, calcium, and zinc.
The Heart-Healthy Benefits of Eggs
Contrary to previous concerns, moderate egg consumption generally does not elevate the risk of heart disease for most individuals. For the majority, consuming an egg a day does not increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, or other cardiovascular ailments.
A controlled study in 2022 investigated the link between egg consumption, metabolic markers, and cardiovascular disease risk. The findings indicated that individuals who consumed a moderate quantity of eggs exhibited elevated levels of apolipoprotein A1, a protein that is a building block of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), often referred to as 'good lipoprotein'. These individuals, in particular, had larger HDL molecules in their bloodstream, which aid in removing cholesterol from blood vessels, thereby offering protection against blockages that may result in heart attacks and strokes.
However, research has also linked egg consumption to a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Boosting Brainpower with Eggs
Eggs are a prime source of choline, a nutrient essential for brain health. Choline supports memory, mood, and cognitive functions. Research suggests that adequate choline intake may lower the risk of cognitive decline in older adults. A single egg provides approximately 147 mg of choline.
Eggs and Eye Health

Eggs contain antioxidants like lutein and zeaxanthin, which protect against age-related macular degeneration and cataracts. Regular egg consumption can contribute to improved eye health, particularly in older populations.
Strong Bones Thanks to Eggs
Eggs are a natural source of vitamin D, which supports calcium absorption for bone health. Adequate vitamin D intake can decrease the risk of osteoporosis, falls, and fractures.
Radiant Hair and Skin
Eggs provide biotin and other B vitamins that promote healthy hair, skin, and nails. Biotin deficiency can cause hair loss, and eggs offer an easy way to increase your intake.
Eggs for Weight Management

Eggs are an excellent source of protein. Being high in protein and low in calories, they promote satiety, keeping you feeling full for longer periods. Their low-calorie content makes them a good choice for those on a weight loss journey. Consuming egg-based breakfasts can help you feel full longer, potentially aiding in weight loss.
Enhancing Muscle Strength and Repair
The high-quality protein in eggs helps in muscle maintenance and recovery, particularly for those focused on fitness. Eggs are a cost-effective protein source, and proteins are essential building blocks for the human body.
Boosting the Immune System
The selenium and zinc present in eggs help to strengthen the immune system. Studies have demonstrated that these minerals enhance immune response and help the body fight infections.
Raising HDL Levels
Eggs are associated with increased levels of HDL (high-density lipoprotein), often referred to as ‘good’ cholesterol, as it helps remove bad cholesterol from the bloodstream. Individuals with higher HDL levels generally have a lower risk of heart disease, stroke, and even complications related to type 2 diabetes.
Newer articles
Older articles
-
 'Would be remarkable to choose someone else if their last knock was a 170'
'Would be remarkable to choose someone else if their last knock was a 170'
-
 Amitabh Bachchan calls working with son Abhishek Bachchan his 'greatest blessing'
Amitabh Bachchan calls working with son Abhishek Bachchan his 'greatest blessing'
-
 Aamir Khan’s Sitaare Zameen Par picks up momentum on release day as last-hour bookings surge past 10,000 tickets
Aamir Khan’s Sitaare Zameen Par picks up momentum on release day as last-hour bookings surge past 10,000 tickets
-
 Are we living inside a black hole? NASA’s James Webb findings stun scientists
Are we living inside a black hole? NASA’s James Webb findings stun scientists
-
 Vivek Oberoi reveals how shifting to Dubai helped him build a Rs 1200 crore real estate empire: ‘This feels more like home now’
Vivek Oberoi reveals how shifting to Dubai helped him build a Rs 1200 crore real estate empire: ‘This feels more like home now’
-
 Jaya Bachchan believes Amitabh Bachchan “gave a better performance” than her in ‘Mili’ - Exclusive
Jaya Bachchan believes Amitabh Bachchan “gave a better performance” than her in ‘Mili’ - Exclusive
-
 IND vs ENG: Ben Stokes bursts out laughing after Rishabh Pant smacks him down the ground for four - watch
IND vs ENG: Ben Stokes bursts out laughing after Rishabh Pant smacks him down the ground for four - watch
-
 Sunjay Kapur’s sister Mandhira shares rare selfie after his funeral: 'We are incomplete without you'
Sunjay Kapur’s sister Mandhira shares rare selfie after his funeral: 'We are incomplete without you'
-
 Priyanka Chopra opens up about leaving daughter Malti Marie in New York to shoot SS Rajamouli’s SSMB29 with Mahesh Babu: ‘I fly back and forth from there’
Priyanka Chopra opens up about leaving daughter Malti Marie in New York to shoot SS Rajamouli’s SSMB29 with Mahesh Babu: ‘I fly back and forth from there’
-
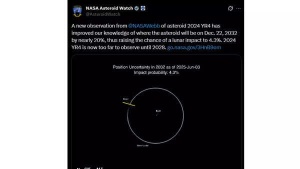 ‘City killer’ asteroid may hit the Moon in December 2032 could threaten satellites around Earth; experts warn
‘City killer’ asteroid may hit the Moon in December 2032 could threaten satellites around Earth; experts warn